DICTUMS IN MANAGEMENT
1.
Even you do no good do no harm
Ventilation of a neonate is a serious enterprise and should be undertaken only if the 5 components of the project are present with optimal proficiency.

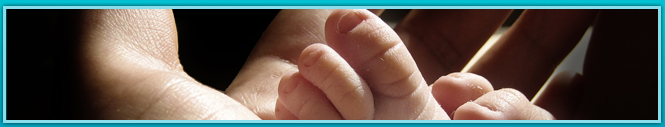
If the survival of Level- II babies exceeds 80% then assisted ventilation is to be considered. Early CPAP use , followed by intact survival of babies above 1.5 kg may be used as a criteria to institute ventilator care. In developing countries poor infrastructure and man power lead to ventilation induced morbidity and mortality. The growing concern is the population of babies with hypoxic sequelae, cerebral palsy and blindness, not to mention ventilator induced lung injury and BronchoPulmonary Dysplasia.
Intact newborn survival should be centerpoint.in management
Training in a tertiary centre for 3 months is reasonable for intact survival of babies above1.5 kg. Anticipatory transfer with Intravenous Fluids , temperature control, glucose homeostasis and transport ventilator to a higher centre is instrumental in central nervous system protection..
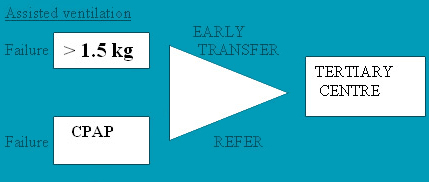
CPAP REVISITED A unit which uses CPAP from birth and subsequently pre and post extubation to optimise FRC has seen reduced incidence of BPD and less severity of BPD in ventilated babies. Our study revealed that 76 % of babies born of 26 weeks gestation onwards in our unit can be managed with CPAP only .
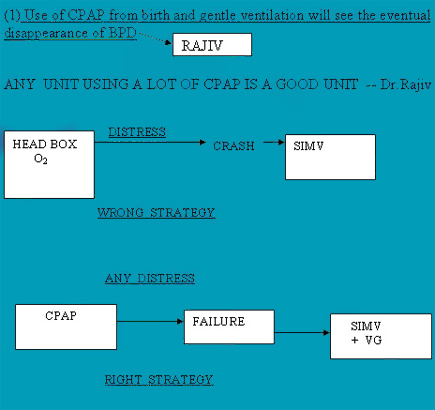
(1) Use of CPAP from birth and gentle ventilation will see the eventual disappearance of BPD
ANY UNIT USING A LOT OF CPAP IS A GOOD UNIT -- Dr.Rajiv
 WHEN IN DOUBT PEEP IT UP
WHEN IN DOUBT PEEP IT UP
The majority of lung diseases in newborn are atelactatic and CPAP, PEEP all contribute to the optimisation of FRC and oxygenation.. PEEP phobia prevent us from using Higher" PEEP to optimize FRC .. In High Frequency Oscillation the entire oxygenation is controlled by CPAP. "Lower PEEP" and high PIP (tidal volume ) are important in the genesis of BPD. We should change our mind set to use higher PEEP in hypoxemic situations.
Atelactatic Diseases - RDS , PPHN , Pneumonia Pulmonary edema, hemorrhage
PEEP could directly improve oxygenation.
Obstructive Diseases - MAS
PEEP is cautiously used but in the range of 4 - 6 cmH2O, as it is an air trapping syndrome. PEEP is not directly proportional to oxygenation.
GETTING OVER THE PROBLEM
In RDS , Pneumonia. Increment in PEEP,CPAP would improve oxygenation and optimise FRC. In BPD and PPHN such a policy could be hazardous. PEEP beyond 8 cmH2O PaO2 is to be used with caution. HFO may be preferred., which could be said to be a modified form of CPAP, colloquially.
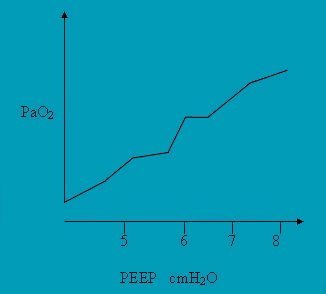 SITTING ON THE FENCE
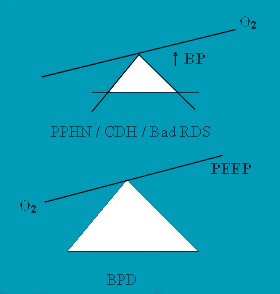
SITTING ON THE FENCE Avoid aggressive management in severe lung diseases especialy when dealing with refractory hypoxemia
e.g. PPHN , CDH , BPD.
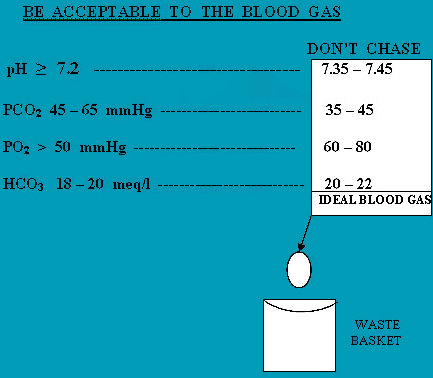
Accept reasonable Blood Gases for the age and disease process at every point of time.
 BE GENTLE TO THE LUNG
BE GENTLE TO THE LUNG
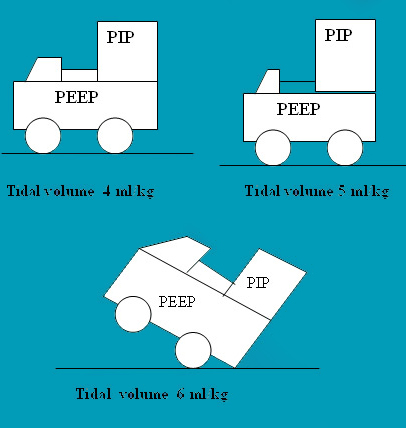
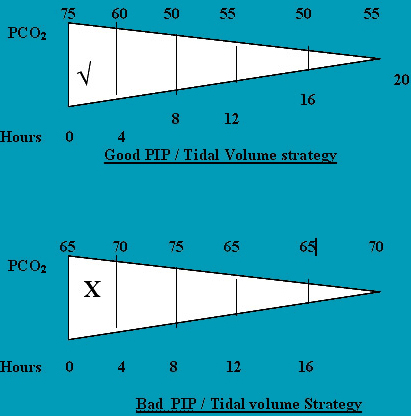
Once ventilation is initiated PEEP is the center point. Once optimised, PIP which controls tidal volume should be accurately targeted. (tidal volume 4 ml/kg ) A tidal volume of 6 ml/kg is recommended but our unit has used 4 ml/kg guideline for about 8 years with good results and almost disappearance of BPD above 650 grams. CO2 can be kept between 50 - 60 mmHg. The current recommendation is a CO2 = 55 mmHg.A blood CO2 of initially 75 mmHg could be accepted and Sequentially but not abruptly reduced to about 50 mmHg . pH > 7.2 is recommended. In the management strategy.
 Back
Back